Fingerprint analysis has been an important tool in criminal investigations for over a century, and its accuracy in identifying suspects has been well-established. However, the question remains: do identical twins have different fingerprints? This article delves into the science and genetics behind fingerprint formation and explores the similarities and differences between identical twins’ fingerprints.
What are fingerprints and how do they form?
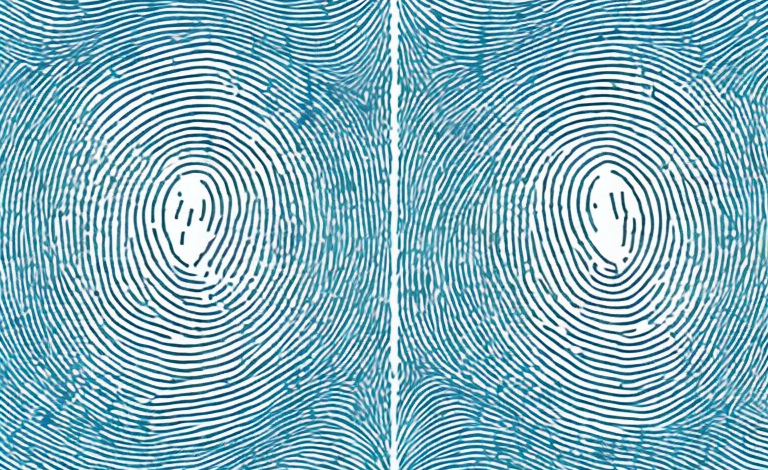
Fingerprints are unique patterns of ridges and valleys on the skin’s surface that form in the womb between 10 and 24 weeks of pregnancy. These patterns are formed due to pressure on the skin from the developing fingers and are influenced by both genetic and environmental factors. Fingerprints are classified into three basic patterns: arches, loops, and whorls.
The science behind identical twins: similarities and differences
Identical twins, also known as monozygotic twins, come from a single fertilized egg that splits in two and develops into two individuals genetically identical to each other. Despite their genetic identity, minor differences in their environment can lead to variations in their physical characteristics. Such differences may include birth weight, eye color, hair color, and even fingerprints.
Studies have shown that identical twins also share similarities in their personality traits, intelligence, and even their risk for certain diseases. This is because their genetic makeup is the same, and therefore they may have similar predispositions to certain conditions.
However, identical twins can also develop differences in their behavior and preferences as they grow older and experience different life events. This is due to the influence of their environment, such as their upbringing, education, and social interactions.
Can identical twins be told apart by their fingerprints?
While identical twins may have similar fingerprints, they are not identical. The ridges on each finger are determined by both genetic and environmental factors, which can lead to subtle differences that may be detectable with close examination. Fingerprint examiners use a variety of techniques to analyze the minutiae, or unique features, of a fingerprint to distinguish between individuals, including identical twins.
However, there are cases where identical twins may have nearly identical fingerprints, making it difficult for even experts to tell them apart. In such cases, other forms of identification, such as DNA testing or facial recognition, may be necessary to determine their identity.
It is also worth noting that fingerprints can change over time due to factors such as aging, injury, or certain medical conditions. This means that even if identical twins had identical fingerprints at birth, they may develop differences later in life that could be used to tell them apart.
Understanding the genetic basis of fingerprint formation
Fingerprints are influenced by a complex interplay of genetic and environmental factors. The genes responsible for fingerprint formation are located on chromosome 4, and variations in the expression of these genes can lead to unique patterns. Twin studies have shown that genetics play a more significant role in determining the pattern of ridges in fingerprints than environmental factors.
Recent research has also identified specific genes that are associated with fingerprint formation. One such gene is called HOXC13, which is responsible for the development of the epidermis, the outermost layer of skin. Mutations in this gene have been linked to abnormal fingerprint patterns, such as the absence of ridges or the presence of extra ridges.
Understanding the genetic basis of fingerprint formation has important implications for forensic science. By analyzing the DNA in a fingerprint, forensic experts can identify individuals with a high degree of accuracy. This has revolutionized criminal investigations and has led to the successful prosecution of many criminals who would have otherwise gone free.
The role of epigenetics in determining fingerprint patterns
Epigenetics, the study of how gene expression can be modified without changing the underlying DNA sequence, may also play a role in determining fingerprint patterns. Studies have shown that exposure to certain environmental factors during development, such as maternal smoking, can result in changes in the expression of the genes responsible for fingerprint formation.
Furthermore, recent research has suggested that epigenetic modifications may also be responsible for the differences in fingerprint patterns between identical twins. While identical twins share the same DNA sequence, their fingerprints can still be distinct from one another. This may be due to differences in the epigenetic modifications that occur during development and throughout their lives.
Understanding the role of epigenetics in fingerprint formation could have important implications for forensic science. By analyzing the epigenetic modifications present in a fingerprint, it may be possible to determine important information about the individual who left the print, such as their age, sex, and even their exposure to certain environmental factors. This could greatly enhance the accuracy and reliability of fingerprint analysis in criminal investigations.
How environmental factors can influence fingerprint development in twins
While genetics play a significant role in determining fingerprint patterns, environmental factors can also influence their development. Factors such as nutrition, temperature, and pressure on the developing fingers during pregnancy can all affect the formation of fingerprints in identical twins, resulting in minor differences in their patterns.
Research has shown that twins who were exposed to different environmental conditions during their development can have significantly different fingerprints. For example, twins who were born at different altitudes or in different climates may have distinct fingerprint patterns due to differences in temperature and humidity levels.
Additionally, certain medications or illnesses during pregnancy can also impact fingerprint development in twins. For instance, exposure to certain drugs or infections can cause abnormalities in the formation of fingerprints, leading to unique patterns in each twin.
Comparing the fingerprints of identical twins raised in different environments
Twin studies have shown that identical twins raised in different environments may have significant differences in their fingerprints, despite their genetic identity. For example, if one twin is exposed to more pressure on their developing fingers during pregnancy, they may have a more pronounced ridge pattern than their sibling raised in a different environment.
Additionally, environmental factors such as diet, exposure to chemicals, and physical activity levels can also impact the development of fingerprints. Studies have found that twins raised in different environments may have differences in the number and shape of their ridges, as well as the overall pattern of their fingerprints. These findings highlight the complex interplay between genetics and environment in shaping human traits.
Are there any instances where identical twins have different fingerprints?
While it is rare, there have been documented cases of identical twins having completely different fingerprints. These instances most commonly occur when one twin develops a skin condition, such as eczema or psoriasis, that alters the ridges on their fingers. In such cases, these twins can be reliably distinguished using fingerprint analysis.
Another rare instance where identical twins can have different fingerprints is when one twin undergoes a surgical procedure that affects the skin on their fingers. For example, if one twin has a skin graft or a finger amputation, their fingerprints may be altered and differ from their twin’s.
It is also important to note that while identical twins share the same DNA, their fingerprints are not solely determined by genetics. Fingerprints are formed in the womb and are influenced by factors such as the position of the fetus, the amount of amniotic fluid, and the pressure on the fingers. Therefore, even without any external factors, identical twins may have slight variations in their fingerprints.
The legal implications of identical twin fingerprints in forensic investigations
The existence of identical twin fingerprints can complicate forensic investigations, particularly when both twins are suspects in a crime. Fingerprint examiners must carefully scrutinize each fingerprint and use advanced technology to detect subtle differences between them to make a reliable identification.
However, the use of identical twin fingerprints as evidence in court has also been a topic of debate. Some argue that the presence of identical twin fingerprints alone is not enough to prove guilt beyond a reasonable doubt, as it is possible for one twin to have left the fingerprint at the crime scene while the other was elsewhere. Others argue that the probability of two unrelated individuals having the same fingerprints is so low that the presence of identical twin fingerprints should be considered strong evidence of guilt.
Using advanced technology to distinguish between identical twin fingerprints
Advanced technology, such as high-resolution imaging and computer algorithms, can aid fingerprint examiners in distinguishing between identical twin fingerprints. Some techniques use sophisticated mathematical calculations to analyze the minutiae of a fingerprint, which may reveal subtle differences between otherwise indistinguishable prints.
One such technique is called “ridge flow mapping,” which involves analyzing the flow and direction of the ridges in a fingerprint. This can reveal differences in the way the ridges curve or intersect, which can be used to differentiate between identical twin prints. Another technique involves using ultraviolet light to reveal hidden details in a fingerprint, such as sweat pores or other unique characteristics that may not be visible to the naked eye.
While these advanced techniques can be helpful in distinguishing between identical twin fingerprints, they are not foolproof. It is still important for fingerprint examiners to exercise caution and use multiple methods to verify the accuracy of their findings, especially in cases where the stakes are high, such as in criminal investigations or court cases.
Debunking myths about identical twin fingerprints and their accuracy in identification
Myths about identical twin fingerprints, such as the notion that they are always identical, have persisted for decades. However, advances in forensic science have revealed the complex nature of fingerprint analysis and the potential for subtle differences among fingerprints of identical twins.
One of the most common misconceptions about identical twin fingerprints is that they are completely identical and cannot be distinguished from one another. However, studies have shown that even though identical twins share the same DNA, their fingerprints can still have slight variations due to environmental factors such as nutrition, injuries, and even the position of the fetus in the womb during development.
Another myth about identical twin fingerprints is that they can be used to frame one twin for a crime committed by the other. However, fingerprint analysis is just one piece of evidence used in criminal investigations and is always considered in conjunction with other evidence such as eyewitness accounts, DNA analysis, and surveillance footage. Additionally, forensic experts are trained to identify the subtle differences between identical twin fingerprints and can distinguish between them with a high degree of accuracy.
Understanding the limitations of fingerprint analysis in criminal investigations involving identical twins
While fingerprint analysis is a powerful tool in criminal investigations, it does have limitations, particularly in cases involving identical twins. The subtle differences between their fingerprints may require careful scrutiny and reliance on other forms of evidence to make a reliable identification.
Future directions for research on fingerprint development and identification in identical twins
Further research is needed to shed light on the genetic and environmental factors that influence fingerprint formation in identical twins. Advances in technology may also improve the accuracy and reliability of fingerprint analysis in cases involving identical twins.
Conclusion: what we know and what we still need to learn about identical twin fingerprints
While identical twins may have similar fingerprints, they are not identical. Fingerprint examiners use a variety of techniques to analyze the minutiae of a fingerprint to distinguish between individuals, including identical twins. However, further research is needed to better understand the genetic and environmental factors that influence fingerprint formation in identical twins, and to develop more sophisticated methods to distinguish between similar prints.